Understanding PMI’s Vision of the Project Manager: A Guide for PMP Exam Takers
If you’re preparing for your PMP exam, it’s essential to understand PMI’s (Project Management Institute) view of a project manager. PMI doesn’t just define project management as a profession—it elevates it to a high level where PMPs (Project Management Professionals) are empowered with tools, authority, and processes to drive projects toward success. This blog helps in defining Project Manager from PMI Perspective insights to help PMP exam takers embody that vision for exam success.
PMI’s Project Manager: The High-Level Vision
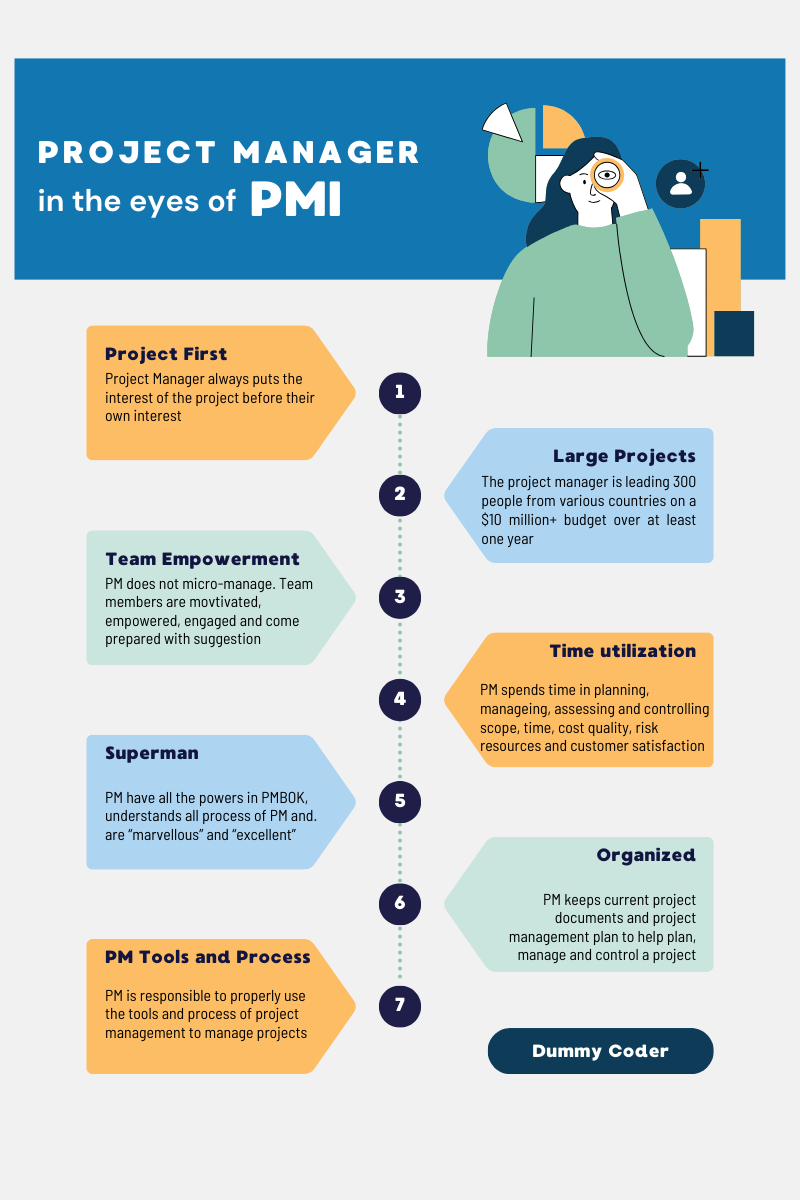
In PMI’s framework, the project manager is the ultimate driver of project success. The project manager keeps the project as the highest priority at all times, ensuring that decisions, resources, and efforts are aligned with project objectives. PMI positions project managers not as micromanagers but as strategic leaders who guide teams, manage stakeholders, and oversee the entire project lifecycle with precision.
PMI emphasizes that project managers:
- Have authority and responsibility: The PMBOK® Guide defines the project manager as the person with the most power within the project environment, entrusted with the responsibility to make key decisions.
- Leverage tools and processes: PMI equips project managers with a comprehensive toolkit of processes and techniques that span Initiating, Planning, Executing, Monitoring & Controlling, and Closing phases.
- Think strategically: A PMI project manager focuses on the big picture, integrating business goals with project outcomes rather than diving into granular details.
Key Traits of PMI’s Project Manager
To embody PMI’s ideal project manager, you need to develop certain traits and behaviors, which are heavily emphasized in the PMP exam:
- Project-Centric Mindset: PMI insists that the project manager prioritizes the project above all else. Decisions should revolve around project success, even when navigating conflicts or compromises.
- Leader, Not Micromanager: PMI’s project manager leads by inspiring and motivating teams, rather than overseeing every small task. Trust and delegation are critical to effective leadership.
- Proactive Problem-Solver: Anticipating risks and addressing challenges head-on are key skills for keeping projects on track.
- Master of PMI Tools: PMI expects project managers to utilize the tools, templates, and methodologies outlined in the PMBOK® Guide to optimize processes and decision-making.
- Ethical and Professional: Integrity is paramount; PMI demands that project managers uphold high ethical standards and treat stakeholders and teams with professionalism.
Tips for PMP Exam Takers: Thinking Like a PMI Project Manager
To excel in the PMP exam, you need to approach scenarios with PMI’s high-level vision in mind. Here are some key strategies:
- Adopt a Project-First Mentality: Ensure every decision and action benefits the project’s objectives and avoid being drawn into unrelated issues.
- Think Big Picture: Avoid micromanaging in situational questions and focus on strategic outcomes.
- Leverage PMBOK® Tools: Reference PMI’s tools and processes in your answers, showing how they help achieve success.
- Prove Leadership Skills: Show how you can lead teams, resolve conflicts, and inspire collaboration.
- Stay Ethical: Always choose the option that reflects PMI’s emphasis on integrity and professionalism.
PMI sets the bar high for project managers, positioning them as empowered leaders equipped with the tools and authority to drive project success. As a PMP exam taker, understanding PMI’s vision will help you navigate the exam with confidence and align your mindset with PMI’s expectations. Think like a project-focused leader who uses every tool and process available, prioritizes ethical decision-making, and inspires teams to achieve project excellence.
This isn’t just preparation for an exam—it’s preparation for a career that exemplifies PMI’s ideals. Step into the role of the project manager PMI envisions, and you’ll not only pass the PMP exam but also elevate your professional potential to new heights.
Here are some questions to revise the concept before you leave:
1. According to PMI, what is the project manager’s primary responsibility?
- Focusing on business-as-usual operations
- Ensuring that all project resources are solely focused on organizational goals
- Keeping the project as the highest priority and aligning resources with project objectives
- Delegating every aspect of project execution to team members
2. How does PMI describe the project manager in the PMBOK® Guide?
- As an administrator responsible for reports and documentation
- As the person with the most authority and decision-making responsibility within the project environment
- As a facilitator of team discussions
- As a neutral party between stakeholders
3. What is one key trait PMI emphasizes for project managers?
- A micromanagement style to ensure every task is completed on time
- Authority without responsibility
- A project-centric mindset that prioritizes project success above all else
- A focus solely on technical aspects of the project
4. Why is it essential for project managers to avoid micromanaging, according to PMI?
- It increases the complexity of managing resources
- It allows stakeholders to assume leadership
- It fosters trust and inspires team members while enabling strategic leadership
- It reduces documentation requirements for the project
5. What does PMI mean by “thinking strategically” as a project manager?
- Focusing on technical deliverables rather than organizational goals
- Aligning business goals with project outcomes and focusing on the big picture
- Constantly revising scope based on team feedback
- Setting daily tasks for team members
6. What is PMI’s perspective on risk management?
- Risks should be addressed only when they are realized
- Risks should be anticipated and addressed proactively to keep the project on track
- Risks are solely the responsibility of stakeholders to resolve
- Risk management is not emphasized in PMI’s framework
7. In PMI’s framework, which of the following is the best example of utilizing PMBOK® tools?
- Following informal communication styles to resolve issues
- Using standard methodologies and processes across all phases of the project life cycle
- Delegating all documentation responsibilities to stakeholders
- Avoiding regular status updates
8. A project manager who exemplifies PMI’s ideal is MOST likely to:
- Avoid using ethical considerations in decision-making
- Focus exclusively on short-term deliverables
- Motivate the team and resolve conflicts while maintaining professionalism
- Keep themselves distant from the team
9. Which of the following is a key aspect of PMI’s view of project success?
- Delivering the project regardless of stakeholder satisfaction
- Ensuring that all conflicts are resolved by the sponsor
- Aligning decisions, resources, and efforts with project objectives
- Delegating all authority to functional managers
10. What should a project manager focus on when resolving conflicts, according to PMI?
- Avoiding decision-making to maintain neutrality
- Aligning conflict resolution efforts with project success and objectives
- Escalating all issues to the project sponsor
- Allowing team members to resolve conflicts independently
11. In PMI’s framework, which leadership style is preferred?
- Directive and controlling
- Inspirational and motivational
- Neutral and passive
- Reactive and detached
12. What is a defining characteristic of PMI’s project manager with respect to tools and methodologies?
- They avoid formal project tools to maintain agility
- They rely solely on past experiences rather than structured frameworks
- They leverage PMBOK® Guide tools and methodologies for effective decision-making
- They allow team members to design their own methods for project execution
13. Why is ethical behavior critical for a project manager, according to PMI?
- It ensures legal compliance and avoids contractual issues
- It builds trust and ensures professionalism in managing teams and stakeholders
- It avoids conflicts during the project closing phase
- It is solely required for obtaining the PMP certification
14. When analyzing a project scenario on the PMP exam, what mindset should the project manager adopt?
- A focus on short-term team dynamics
- A project-first mentality prioritizing objectives above all else
- A passive approach to maintain neutrality
- A reliance on ad-hoc solutions rather than processes
15. Which of the following tips is NOT aligned with PMI’s vision for the project manager during the PMP exam?
- Thinking big picture and avoiding micromanagement
- Resolving conflicts without considering project objectives
- Leveraging PMBOK® tools for optimizing processes
- Prioritizing ethical decision-making
1. C. Keeping the project as the highest priority and aligning resources with project objectives
2. B. As the person with the most authority and decision-making responsibility within the project environment
3. C. A project-centric mindset that prioritizes project success above all else
4. C. It fosters trust and inspires team members while enabling strategic leadership
5. B. Aligning business goals with project outcomes and focusing on the big picture
6. B. Risks should be anticipated and addressed proactively to keep the project on track
7. B. Using standard methodologies and processes across all phases of the project life cycle
8. C. Motivate the team and resolve conflicts while maintaining professionalism
9. C. Aligning decisions, resources, and efforts with project objectives
10. B. Aligning conflict resolution efforts with project success and objectives
11. B. Inspirational and motivational
12. C. They leverage PMBOK® Guide tools and methodologies for effective decision-making
13. B. It builds trust and ensures professionalism in managing teams and stakeholders
14. B. A project-first mentality prioritizing objectives above all else
15. B. Resolving conflicts without considering project objectives
Let me know if you’d like further clarification on any of the questions or answers!